Condensed Matter Theoretical Physics
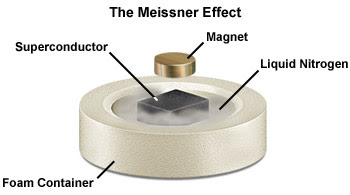
Superconductivity is associated with magnetic flux expulsion, which in turn causes magnetic levitation in the above demonstration (see video). J. Robert Schrieffer was the co-recipient of the Nobel Prize for developing the BCS theory of superconductivity. Three decades ago, defying many expectations, new forms of quantum matter were discovered including unconventional superconductors and quantum Hall states. We now understand that just like a large collection of atoms can organize itself into solid, liquid or gas phase, quantum matter can organize itself into "valence bond solid", "spin liquid" and "Fermi gas" phases among many others. The quest to understand such phases and the conditions under which they occur has spawned the study of correlated systems. These include, but are not restricted to, moire systems (e.g. "twisted graphene"), quantum magnets, quantum Hall states, topological matter, metal-insulator transitions and more.
Our group maintains active theoretical research programs at the forefront of both "hard" and "soft" condensed matter physics. The former strives to understand phenomena arising from interplay of quantum mechanics and interactions among an extremely large number of constituents. On the other hand, the latter studies states of matter dominated by energies of the order of room temperature where quantum aspects are generally unimportant. Nevertheless, condensation of matter into complex yet organized collective states is a common theme unifying the two subfields. In both areas, scientific computation often has an important role to play.

Examples "hard" theory are studies ofhigh-temperature superconductors (Manousakis, Vafek, Yang)
heavy Fermion systems (Dobrosavljevic, Schlottmann)
glassy and complex behavior of correlated systems (Dobrosavljevic)
metal-insulator transitions (Dobrosavljevic)
one-dimensional electron system (Schlottmann, Yang)
quantum computation (Bonesteel)
quantum criticality (Bonesteel, Dobrosavljevic, Manousakis, Schlottmann, Vafek, Yang, Changlani)
quantum Hall effects (Bonesteel, Manousakis, Vafek, Yang)
quantum liquids and solids (Manousakis, Changlani)
quantum magnetism (Changlani)
transition metal oxides (Dobrosavljevic, Schlottmann)
"twisted" moire materials (Vafek, Lewandowski)
Examples of "soft" theory are studies ofequilibrium and nonequilibrium computational statistical mechanics (Rikvold)
Biological systems (Rikvold)
More details are available at web pages of individual faculty.
Centers, Research Groups & Facilities:National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, the preeminent magnet research facility in the world (click here for overview video).
Condensed Matter and Materials Physics (CMMP)
Department of Scientific Computing (SC)
Our group maintains active theoretical research programs at the forefront of both "hard" and "soft" condensed matter physics. The former strives to understand phenomena arising from interplay of quantum mechanics and interactions among an extremely large number of constituents. On the other hand, the latter studies states of matter dominated by energies of the order of room temperature where quantum aspects are generally unimportant. Nevertheless, condensation of matter into complex yet organized collective states is a common theme unifying the two subfields. In both areas, scientific computation often has an important role to play.

Examples "hard" theory are studies ofhigh-temperature superconductors (Manousakis, Vafek, Yang)
heavy Fermion systems (Dobrosavljevic, Schlottmann)
glassy and complex behavior of correlated systems (Dobrosavljevic)
metal-insulator transitions (Dobrosavljevic)
one-dimensional electron system (Schlottmann, Yang)
quantum computation (Bonesteel)
quantum criticality (Bonesteel, Dobrosavljevic, Manousakis, Schlottmann, Vafek, Yang, Changlani)
quantum Hall effects (Bonesteel, Manousakis, Vafek, Yang)
quantum liquids and solids (Manousakis, Changlani)
quantum magnetism (Changlani)
transition metal oxides (Dobrosavljevic, Schlottmann)
"twisted" moire materials (Vafek, Lewandowski)
Examples of "soft" theory are studies ofequilibrium and nonequilibrium computational statistical mechanics (Rikvold)
Biological systems (Rikvold)
More details are available at web pages of individual faculty.
Centers, Research Groups & Facilities:National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, the preeminent magnet research facility in the world (click here for overview video).
Condensed Matter and Materials Physics (CMMP)
Department of Scientific Computing (SC)
#CondensedMatterPhysics #TheoreticalPhysics #QuantumMechanics #QuantumPhenomena #QuantumMaterials #ElectronicStructure #ManyBodyPhysics #Superconductivity #TopologicalInsulators #QuantumHallEffect #StronglyCorrelatedSystems #Spintronics #Magnetism



Comments
Post a Comment